Centrifugal pumps are vital components in various industrial processes, playing a pivotal role in fluid transport. To ensure their seamless operation and longevity, regular and systematic maintenance is paramount. This comprehensive maintenance checklist provides a structured approach to safeguarding the efficiency and reliability of your centrifugal pump system.
From daily visual inspections to annual overhauls, each task is meticulously outlined to guide you through the process. By adhering to this checklist, you not only prolong the life of your pump but also enhance its performance, ultimately reducing operational costs.
Incorporating safety precautions, routine tasks, and periodic checks, this checklist encompasses the full spectrum of maintenance activities. Remember, proactive maintenance not only prevents unexpected breakdowns but also contributes to a more sustainable and cost-effective operation.
Let’s embark on this journey to maintain the heart of your fluid management system – the centrifugal pump.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of centrifugal pumps is crucial for ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. It helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, reduces energy consumption, and lowers overall operating costs. Neglecting maintenance can lead to severe damage and costly repairs.
Prolonging Pump Life and Efficiency
Proper maintenance practices can significantly extend the lifespan of a centrifugal pump. By addressing issues early on, you can prevent wear and tear, prolonging the pump’s operational life. Additionally, a well-maintained pump operates more efficiently, leading to energy savings.
Safety Considerations
Safety should always be a top priority when performing maintenance tasks. Ensure that lockout/tagout procedures are followed to prevent accidental start-ups. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and hearing protection. Also, consider any environmental factors that may impact maintenance procedures.
General Precautions
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Before any maintenance work, it’s essential to isolate the pump from its power source. Lockout/tagout procedures ensure that the pump cannot be started accidentally. This involves physically locking switches or valves and tagging them with a warning.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing the correct PPE is crucial for personal safety during maintenance. This may include safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection, and appropriate footwear. The specific PPE required will depend on the nature of the maintenance task.
Environmental Considerations
Consider the environment in which the pump operates. For example, if the pump is in a hazardous location, special precautions may be needed. Additionally, if the pump handles hazardous materials, take extra care to contain and manage them during maintenance.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Lubrication
1. Bearing Lubrication
Regularly lubricate the pump’s bearings according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Use the recommended lubricant and ensure it’s at the correct level for optimal performance.
2. Seal Lubrication
If your pump has seals, lubricate them as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. Properly lubricated seals help maintain a tight seal, preventing leaks.
Alignment Checks
Check the alignment of the pump with its driver (usually an electric motor). Misalignment can lead to premature wear and decreased efficiency. Use precision alignment tools to rectify any issues.
Vibration Analysis
Periodically monitor the pump’s vibration levels. Elevated vibration can indicate misalignment, bearing wear, or other issues. Analyze the data to identify and address potential problems.
Temperature Monitoring
Regularly monitor the temperature of key components such as bearings and the motor. Elevated temperatures can indicate problems like inadequate lubrication or bearing wear.
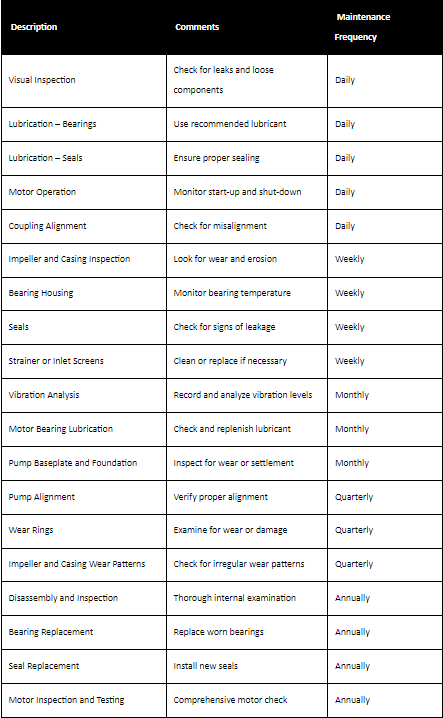
Daily Checks
1. Visual Inspection
- Check for Leaks: Inspect all connections, seals, and joints for any signs of leakage. Address any leaks promptly to prevent further damage.
- Check for Loose or Damaged Components: Look for any visibly loose or damaged parts, including bolts, nuts, and brackets. Tighten or replace as necessary.
2. Lubrication
- Verify Proper Lubrication Levels: Ensure that all lubrication points are adequately lubricated. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended lubricant and quantity.
3. Motor Operation
- Ensure Smooth Start-Up and Shut-Down: Monitor the pump’s start-up and shut-down sequences. Any irregularities may indicate motor or electrical issues.
- Monitor Motor Temperature: Touch the motor to check for abnormal heat. If it feels excessively hot, investigate further.
4. Coupling Alignment
- Check for Misalignment: Inspect the coupling for any signs of misalignment, such as gaps or visible offsets. Correct any misalignment to prevent damage.
Weekly Checks
1. Impeller and Casing Inspection
- Check for Wear and Erosion: Inspect the impeller and casing for signs of wear, erosion, or corrosion. Pay special attention to areas near the inlet and outlet.
2. Bearing Housing
- Monitor Bearing Temperature: Use a temperature gun to measure the temperature of the bearing housing. Elevated temperatures can indicate bearing issues.
3. Seals
- Inspect for Leakage: Check the seals for any signs of leakage. Address any leaks promptly to maintain the integrity of the seal.
4. Strainer or Inlet Screens
- Clean or Replace if Necessary: If applicable, inspect and clean or replace strainers or inlet screens to ensure unimpeded flow.
Monthly Checks
1. Vibration Analysis
- Record and Analyze Vibration Levels: Use a vibration analyzer to record and analyze vibration levels. Compare readings to baseline values to identify changes.
2. Motor Bearing Lubrication
- Check and Replenish Lubricant: Verify the lubrication level of the motor bearings and replenish if needed.
3. Coupling Alignment
- Verify Proper Alignment: Recheck the alignment of the coupling to ensure it remains correctly aligned.
4. Pump Baseplate and Foundation
- Inspect for Wear or Settlement: Examine the pump’s baseplate and foundation for any signs of wear, settlement, or shifting. Address any issues promptly to maintain stability.
Quarterly Checks
1. Check Pump Alignment
- Verify that the pump remains properly aligned with its driver. Correct any misalignment as necessary.
2. Inspect Wear Rings
- Examine wear rings for signs of wear or damage. Replace if necessary to maintain optimal performance.
3. Inspect Impeller and Casing Wear Patterns
- Check the impeller and casing for wear patterns. Irregular wear may indicate flow issues or misalignment.
Annual Checks
1. Disassembly and Inspection
- Disassemble the pump for a thorough internal inspection. Examine all components for wear, corrosion, or damage.
2. Bearing Replacement
- Replace bearings as part of regular maintenance to prevent failures and extend the pump’s lifespan.
3. Seal Replacement
- Install new seals to maintain a tight, leak-free system.
4. Motor Inspection and Testing
- Conduct a comprehensive inspection of the motor, including electrical connections, insulation, and winding condition. Test motor performance to ensure it meets specifications.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
1. Cavitation
- Identify and address the root cause of cavitation, which can lead to damage of impellers and other components.
2. Overheating
- Investigate the cause of overheating, which may be due to factors like inadequate lubrication, misalignment, or motor issues.
3. Low Flow or Pressure
- Troubleshoot and resolve issues causing low flow or pressure, such as clogs, worn impellers, or problems with the driver.
4. Excessive Vibration
- Analyze the source of excessive vibration, which can be due to misalignment, bearing wear, or other mechanical issues.
Record Keeping
1. Maintenance Logs
- Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities. This includes dates, tasks performed, parts replaced, and any issues identified.
2. Repairs and Replacements
- Document all repairs and component replacements. Note the reason for the repair, the parts used, and any adjustments made.
3. Trend Analysis
- Use maintenance records to identify trends in pump performance. This can help predict future maintenance needs and optimize scheduling.
Conclusion
1. Importance of Adhering to Maintenance Schedule
- Emphasize the significance of following the maintenance schedule. Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the pump’s reliability and longevity.
2. Benefits of Proper Centrifugal Pump Maintenance
- Summarize the benefits of thorough and regular maintenance. These include increased pump efficiency, extended lifespan, and reduced operating costs.
Remember, this Centrifugal Pump Maintenance Checklist is a comprehensive guide, but always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific maintenance procedures and intervals. Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the continued reliable operation of your centrifugal pump.
Recent Posts

A Comprehensive Guide to Types of Water Pumps and Their Applications
Introduction Water pumps are indispensable

The Complete Guide to Water Pumps: Types, Uses, and Maintenance
Water is life, and the

Comprehensive Guide to Split Case Pumps
Split case pumps are a


