Chemical feed pumps, also known as metering pumps or dosing pumps, play a crucial role in numerous industries by precisely delivering chemicals in controlled quantities. These pumps are instrumental in applications where accurate and consistent dosing of chemicals is essential, such as water treatment, pharmaceutical manufacturing, agriculture, and industrial processes.
Importance of Chemical Feed Pumps:
Chemical feed pumps are designed to handle a wide range of chemicals, ensuring the proper treatment and processing of various substances in different industrial settings. Their significance lies in their ability to maintain accuracy and reliability in delivering chemicals, contributing to the efficiency and effectiveness of numerous processes.
Alternative Names:
- Metering Pumps: These pumps are recognized for their capability to meter or measure precise amounts of chemicals, providing accuracy in dosing applications.
- Dosing Pumps: The term “dosing” emphasizes the controlled and measured delivery of chemicals, highlighting the precision of these pumps.
A chemical feed pump is a specialized type of pump designed to accurately inject specific quantities of chemicals into various fluids, such as water, gas, or steam. Unlike regular pumps that primarily focus on moving large volumes of fluid, a chemical feed pump places a strong emphasis on precise dosing.
The key function of a chemical feed pump is to deliver controlled amounts of chemicals into a system with high accuracy. This is crucial in applications where the correct dosage of chemicals is essential for achieving desired results, such as water treatment, industrial processes, or agricultural applications.
Positive displacement pumps play a vital role in the precise control of chemical feed pumps. These pumps operate by trapping a fixed volume of fluid and then displacing it into the discharge pipe. This results in a continuous and consistent flow of fluid, allowing for accurate dosing. Positive displacement pumps are particularly advantageous for applications where precise control of chemical injection is critical, as they provide a reliable and repeatable method of delivering chemicals in a measured manner.
In summary, a chemical feed pump is a specialized pump designed for accurate chemical dosing, distinguishing it from regular pumps that prioritize high flow rates. The use of positive displacement pumps enhances the precision of chemical feed pumps, ensuring controlled and consistent injection of chemicals into various fluids.
Chemical Feed Pump Working Principle:
A chemical feed pump is a crucial component in various industries where accurate and controlled chemical dosing is essential. It typically consists of a pump head, drive mechanism, and check valves. Let’s delve into the general working principle and the main components:
1. Pump Head:
The pump head is the core of the chemical feed pump. It houses the mechanisms responsible for drawing in and pushing out the chemical. The type of mechanism used in the pump head determines the pump’s classification (e.g., diaphragm, piston, peristaltic).
2. Drive Mechanism:
The drive mechanism powers the pump head, causing the necessary movements for the intake and discharge of chemicals. It ensures a consistent and controlled flow rate. The drive mechanism can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic, depending on the specific pump design.
3. Check Valves:
Check valves play a crucial role in maintaining the direction of chemical flow. They prevent backflow, ensuring that the chemical moves in the intended direction. Typically, chemical feed pumps have inlet and outlet check valves.
Types of Pump Mechanisms:
A. Diaphragm Pump:
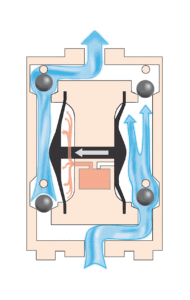
diaphragm pump diagram
Working Principle:
- A flexible diaphragm moves back and forth, creating a pumping action.
- As the diaphragm flexes, it draws in chemicals through the inlet check valve.
- On the return stroke, the diaphragm pushes the chemical out through the outlet check valve.
B. Piston Pump:
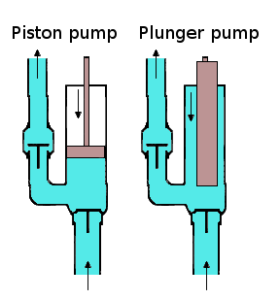
piston pump diagram
Working Principle:
- A piston moves within a cylinder, creating suction and pressure cycles.
- During the suction phase, the piston draws in chemical through the inlet check valve.
- As the piston compresses, the chemical is forced out through the outlet check valve.
C. Peristaltic Pump:
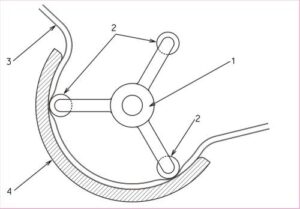
peristaltic pump diagram
Working Principle:
- Rotating rollers compress a flexible tube, creating a peristaltic squeezing motion.
- As the tube is squeezed, it propels the chemical through the pump.
- The alternating compression and relaxation of the tube generate a pulsatile flow.
Applications of Chemical Feed Pumps:
1. Water Treatment Plants (Chlorine Injection for Disinfection):
- Role: Chemical feed pumps are essential in water treatment plants for injecting chlorine into the water. Chlorine is a common disinfectant used to kill bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms in drinking water.
- Benefits: Ensures the safety of the water supply by effectively disinfecting it, preventing the spread of waterborne diseases.
2. Chemical Processing Plants (Precise Addition of Reagents):
- Role: Chemical feed pumps play a crucial role in chemical processing plants by precisely adding reagents to chemical reactions. This ensures accuracy and consistency in the production process.
- Benefits: Enables control over chemical reactions, leading to higher product quality, reduced waste, and increased efficiency in manufacturing processes.
3. Power Plants (Boiler Water Treatment):
- Role: In power plants, chemical feed pumps are used for boiler water treatment. They inject chemicals into the boiler feedwater to prevent corrosion, scale formation, and microbial growth, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the boiler system.
- Benefits: Extends the lifespan of boiler components, improves energy efficiency, and reduces the risk of equipment failure.
4. Agriculture (Irrigation Systems with Fertilizer Injection):
- Role: Chemical feed pumps are employed in agriculture for injecting fertilizers into irrigation systems. This allows for precise control of nutrient levels in the soil, promoting plant growth and maximizing crop yields.
- Benefits: Optimizes the use of fertilizers, minimizes environmental impact, and enhances crop productivity.
5. Food and Beverage Industry (Ingredient Dosing):
- Role: In the food and beverage industry, chemical feed pumps are used for dosing precise amounts of ingredients into production processes. This ensures the consistency and quality of the final products.
- Benefits: Maintains product quality, reduces production waste, and enhances the efficiency of food and beverage manufacturing.
6. Oil and Gas Production (Chemical Injection for Enhanced Oil Recovery):
- Role: Chemical feed pumps are vital in oil and gas production for injecting chemicals into wells to enhance oil recovery. These chemicals can alter the viscosity of the oil, improve flow, and increase overall extraction efficiency.
- Benefits: Maximizes oil recovery from reservoirs, increases production rates, and extends the economic life of oil and gas fields.
In all these applications, chemical feed pumps play a pivotal role in ensuring the accurate and controlled addition of chemicals, contributing to process efficiency, product quality, and environmental sustainability.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Chemical Feed Pump:
Selecting the right chemical feed pump is crucial for efficient and safe chemical dosing in various industrial processes. Here are key considerations to keep in mind:
1. Flow Rate Requirements:
- Determine the required flow rate based on the application’s needs.
- Ensure the pump can handle variations in flow rates if necessary.
2. Pressure Needs:
- Identify the system’s pressure requirements.
- Choose a pump that can provide the necessary pressure for proper chemical injection.
3. Chemical Compatibility:
- Assess the compatibility of the pump materials with the chemicals being used.
- Consider the pump’s resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation.
4. Material of Construction:
- Select materials that withstand the corrosive nature of the chemicals.
- Common materials include stainless steel, plastic, and specialty alloys.
5. Control Options:
- Evaluate the available control options for accurate dosing.
- Options may include manual adjustment, digital controls, or integration with a process control system.
6. Maintenance Requirements:
- Consider ease of maintenance and access to critical components.
- Opt for pumps with features like easy disassembly for cleaning and routine maintenance.
In conclusion, chemical feed pumps play a pivotal role in diverse industries, offering precise control over the dosage and distribution of chemicals. Their significance extends to sectors like water treatment, manufacturing, and agriculture, where accurate chemical dispensing is crucial for operational success. The advantages of utilizing chemical feed pumps are multi-faceted.
Firstly, these pumps provide unparalleled precision, ensuring that chemicals are delivered in exact quantities, minimizing waste and optimizing processes. Secondly, the enhanced efficiency they bring to chemical dispensing operations translates into cost savings and resource optimization for industries. Additionally, chemical feed pumps contribute to safety by minimizing the risk of human error associated with manual dosing.
In light of these benefits, it is imperative for professionals across industries to recognize the transformative impact that chemical feed pumps can have on their operations. A call to action is extended to readers, urging them to delve deeper into the intricacies of specific pump options available in the market. Furthermore, consulting with pump experts can provide invaluable insights tailored to individual industry requirements, fostering a more informed and strategic approach to chemical dispensing solutions. By staying informed and embracing innovative pumping technologies, industries can unlock new levels of efficiency, safety, and overall operational excellence.
Recent Posts

A Comprehensive Guide to Types of Water Pumps and Their Applications
Introduction Water pumps are indispensable

The Complete Guide to Water Pumps: Types, Uses, and Maintenance
Water is life, and the

Comprehensive Guide to Split Case Pumps
Split case pumps are a


