Chemical injection pumps play a pivotal role in various industries, serving as indispensable tools for precise and controlled delivery of chemicals. These pumps are designed to handle a diverse range of substances, from corrosive chemicals to polymers, making them crucial in ensuring efficient processes across different sectors.
What is a chemical injection pump?
Chemical injection pump is a specialized device used to transfer and inject chemicals into a system or process with accuracy and reliability. These pumps are engineered to withstand the challenges posed by corrosive and abrasive substances, ensuring a seamless and controlled flow of chemicals in diverse industrial applications.
The primary purpose of a chemical injection pump is to facilitate the controlled introduction of chemicals into a system. This can involve adding specific substances to water treatment processes, injecting corrosion inhibitors into pipelines, or introducing chemicals for sanitization purposes. The applications of chemical injection pumps are widespread, ranging from oil and gas production to water treatment plants, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and various other industrial settings.
The importance of chemical injection pumps cannot be overstated, as they contribute significantly to the efficiency, safety, and reliability of industrial processes. In the oil and gas sector, for instance, these pumps play a crucial role in enhancing production and protecting equipment from corrosion. In water treatment plants, chemical injection pumps are instrumental in maintaining water quality and preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms. Industries such as pharmaceuticals rely on these pumps for precise dosing during manufacturing processes, ensuring product quality and compliance with stringent standards.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of chemical injection pumps, it becomes evident that their role extends beyond mere conveyance of substances; they are integral components in maintaining the integrity and functionality of critical industrial processes. In the following sections, we will explore the working mechanisms of these pumps, their types, and the diverse applications that highlight their versatility in meeting the specific needs of different industries.
Purpose and Applications:
These pumps serve a critical role in numerous industries by enabling the controlled addition of chemicals for various purposes. Here are some key applications:
Oil and Gas Industry:
- Corrosion inhibition (protecting pipelines and equipment)
- Hydrate prevention (ensuring smooth flow of gas and liquids)
- Scale removal (maintaining wellbore and pipeline integrity)
- Enhanced oil recovery (increasing oil production)
Water Treatment:
- Disinfection (eliminating harmful bacteria and pathogens)
- pH adjustment (optimizing water quality for specific needs)
- Coagulation and flocculation (removing suspended solids)
Chemical Processing:
- Metering of reactants (ensuring precise ratios for desired reactions)
- Catalyst addition (speeding up chemical reactions)
- pH control (maintaining optimal conditions for processes)
Food and Beverage Industry:
- Adding flavors, preservatives, and colorants
- Sanitizing and sterilizing equipment and products
- Dosing CO2 for carbonation
Other Applications:
- Pharmaceutical industry (precise dosing of ingredients in medications)
- Agriculture (injecting fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides)
- Power generation (adding corrosion inhibitors and pH adjusters)
Importance in Various Industries:
Chemical injection pumps play a crucial role in ensuring process efficiency, product quality, and safety across various industries. Their precise control capabilities contribute to:
- Increased productivity: By optimizing processes and preventing downtime due to equipment issues.
- Enhanced product quality: By accurately injecting the right chemicals at the right dosage for desired outcomes.
- Improved safety: By safely handling hazardous chemicals and minimizing environmental impact.
- Reduced operational costs: By optimizing chemical usage and minimizing waste.
In essence, chemical injection pumps are essential tools for various industries, contributing significantly to efficient and safe operations.
II. Working Principle of a Chemical Injection Pump
Chemical injection pumps operate through various mechanisms, each with its own advantages and suited for specific applications. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
A. Diaphragm Pump:
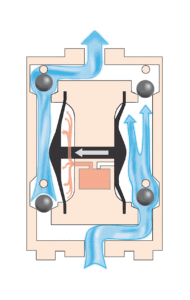
- Mechanism: A flexible diaphragm separates the fluid chamber from the drive mechanism (air or hydraulic pressure). As the diaphragm expands and contracts, it creates suction, drawing in and pushing out the fluid.
- Advantages:
- Leak-free design, ideal for harsh chemicals.
- Capable of handling high pressures and viscosities.
- Self-priming and easy to maintain.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited flow rates compared to other types.
- Pulsating flow may require pulsation dampeners.
2. Piston Pumps:
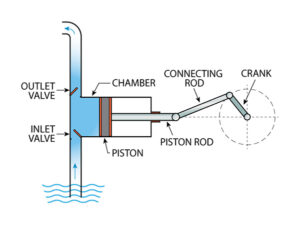
image source: https://blog.chesterton.com/sealing/reciprocating-pump-applications-and-benefits/
- Mechanism: A piston reciprocates within a cylinder, creating pressure to push the fluid out. Check valves regulate flow direction.
- Advantages:
- High flow rates and pressures achievable.
- Precise metering capabilities.
- Can handle abrasive and viscous fluids.
- Disadvantages:
- More complex design and require regular maintenance.
- Internal seals can be susceptible to wear and tear.
- Pulsating flow may require pulsation dampeners.
3. Gear Pumps:
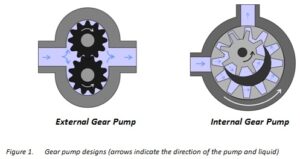
image source: https://www.michael-smith-engineers.co.uk/resources/useful-info/external-gear-pumps
- Mechanism: Two intermeshing gears trap and move fluid between their teeth. The meshing action creates a positive displacement, forcing the fluid out.
- Advantages:
- Simple design and easy to maintain.
- Can handle high viscosities and shear-sensitive fluids.
- Smooth, continuous flow without pulsation.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited pressure capabilities compared to other types.
- Internal clearances can lead to internal leakage.
- Not ideal for abrasive fluids due to potential gear wear.
IV. Key Considerations When Choosing a Chemical Injection Pump: Selecting the Right Tool for the Job
Choosing the right chemical injection pump for your specific application is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Flow Rate and Pressure Requirements:
- Flow rate: Determine the desired volume of chemical you need to inject per unit of time (e.g., gallons per minute, liters per hour).
- Pressure: Consider the pressure required to overcome resistance in the injection line and deliver the chemical to the desired location.
Matching the pump’s capabilities to your requirements ensures accurate dosing and avoids inefficiencies or potential equipment damage.
2. Chemical Compatibility:
- Chemical properties: Identify the specific chemicals you will be injecting, including their viscosity, abrasiveness, and potential corrosiveness.
- Pump material: Choose a pump with materials compatible with the chemicals being handled to prevent leaks, corrosion, and contamination.
- Chemical resistance charts: Consult manufacturers’ charts to identify pumps with suitable material construction for your specific chemicals.
Ensuring compatibility minimizes safety risks, protects your equipment, and maintains product quality.
3. Safety Features:
- Pressure relief valves: Protect against overpressure situations that could damage the pump or piping.
- Leak detection sensors: Alert you to potential leaks for prompt action and spill prevention.
- Emergency shutdown systems: Allow for quick shut-off in case of malfunctions or safety hazards.
- Explosion-proof models: Choose explosion-proof pumps if handling flammable or volatile chemicals.
Prioritizing safety features minimizes risks to personnel, equipment, and the environment.
4. Ease of Maintenance:
- Accessibility: Consider the ease of accessing the pump for maintenance tasks like cleaning, refilling, and replacing parts.
- Spare parts availability: Ensure readily available spare parts to minimize downtime in case of repairs.
- Serviceability: Choose a pump with a design that facilitates easy maintenance and repair procedures.
Easy maintenance reduces operational costs and ensures the pump’s long-term reliability.
By carefully considering these key factors, you can select the optimal chemical injection pump that meets your specific needs and ensures efficient, safe, and cost-effective operation.
V. Conclusion: Chemical Injection Pumps – Precision Dosing for Diverse Applications
Chemical injection pumps have emerged as essential tools across various industries, playing a crucial role in precisely controlling the introduction of chemicals into fluid streams. Here’s a quick recap of their key points:
- Precise Dosing: Unlike regular pumps, they excel at accurately metering and injecting specific chemicals under varying pressure conditions.
- Wide Range of Applications: They find use in industries like oil and gas, water treatment, chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and power generation.
- Essential Benefits: They contribute to enhanced product quality, improved process efficiency, increased safety, and reduced operational costs.
- Key Selection Factors: Flow rate, pressure, chemical compatibility, safety features, and ease of maintenance are crucial considerations when choosing the right pump.
Chemical injection pumps offer remarkable versatility:
- Handling diverse chemicals: From harsh chemicals in oil and gas to sensitive ingredients in pharmaceuticals, they cater to various needs.
- Accommodating varying pressures and flow rates: They meet diverse application requirements, from high-pressure injection in pipelines to precise dosing in chemical reactions.
In essence, chemical injection pumps stand as powerful tools for ensuring:
- Efficiency: Optimized processes and maximized yields.
- Quality: Consistent results and adherence to standards.
- Safety: Minimized risks to personnel, equipment, and the environment.
- Cost-effectiveness: Optimized chemical usage and minimized waste.
By understanding their working principles, applications, and key selection factors, we can leverage these versatile pumps to their full potential, contributing to success across various industries.
Recent Posts

A Comprehensive Guide to Types of Water Pumps and Their Applications
Introduction Water pumps are indispensable

The Complete Guide to Water Pumps: Types, Uses, and Maintenance
Water is life, and the

Comprehensive Guide to Split Case Pumps
Split case pumps are a


