Centrifugal pumps are among the most widely used types of pumps in various industries. They are designed to move liquids from one place to another by converting mechanical energy from a motor into kinetic energy, which drives the fluid through the pump and into the discharge pipe. Centrifugal pumps are commonly used in industrial, domestic, and agricultural applications due to their versatility, simplicity, and efficiency.
Definition of centrifugal pumps
Centrifugal pumps are mechanical devices used to transport fluids by converting mechanical energy from an external source (e.g., an electric motor) into kinetic energy in the fluid being pumped. They work by using a rotating impeller to create a centrifugal force that moves the fluid through the pump and into the discharge pipe.
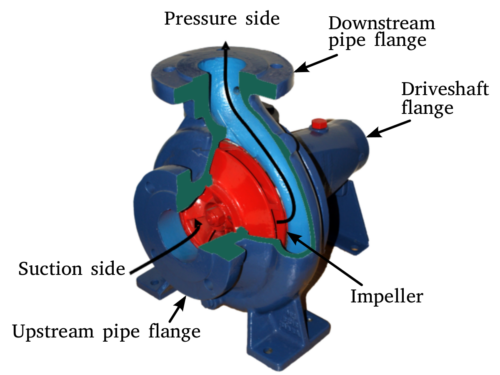
Mechanism of Centrifugal Pumps:
The mechanism of a centrifugal pump is relatively simple. It consists of three main components: an impeller, a casing, and a shaft. The impeller is a rotating component that contains blades or vanes that move the fluid. The casing is a stationary component that surrounds the impeller and guides the fluid to the discharge point. The shaft connects the impeller to the motor that rotates it.
When the impeller rotates, it creates a centrifugal force that moves the fluid from the center of the impeller to the outer edge. As the fluid moves through the casing, it gains momentum and pressure. Finally, it is discharged from the pump through the discharge port.
Importance of centrifugal pumps in various industries
Centrifugal pumps are essential in various industries, including chemical, petrochemical, food and beverage, water and wastewater treatment, power generation, mining, and construction. They are used to transfer fluids such as water, chemicals, fuels, and oils from one place to another. Without centrifugal pumps, many industrial processes would be inefficient or impossible.
II. How centrifugal pumps work
A. Principle of operation
Centrifugal pumps work by converting mechanical energy from a motor into kinetic energy in the fluid being pumped. The impeller rotates at high speed, creating a centrifugal force that pushes the fluid from the center of the impeller to the outer edges. As the fluid moves through the impeller, its velocity increases, and it is directed towards the discharge port by the casing. The kinetic energy of the fluid is then converted into pressure energy as it exits the pump.
B. Key components and their functions
The impeller is the most critical component of a centrifugal pump since it is responsible for transferring energy to the fluid. Impellers come in various shapes and sizes, and their design depends on the type of fluid being pumped, the desired flow rate, and the head pressure. The casing is another essential component of a centrifugal pump since it guides the flow of fluid and creates pressure. Casing design varies according to the pump’s intended application and the fluid being pumped. The suction and discharge ports are also critical since they determine the direction of fluid flow.
C. Types of centrifugal pumps
Centrifugal pumps come in various types, including end suction pumps, inline pumps, multistage pumps, self-priming pumps, and submersible pumps. The choice of pump type depends on the specific application, the desired flow rate, and the head pressure.
Types of Centrifugal Pumps:
- Single-stage Centrifugal Pumps: These pumps have a single impeller and are used for low-pressure applications, such as irrigation and drainage.
- Multi-stage Centrifugal Pumps: These pumps have multiple impellers and are used for high-pressure applications, such as water supply and fire protection.
- Axial-flow Centrifugal Pumps: These pumps have an impeller that rotates parallel to the pump axis and is used for high flow rate applications.
- Radial-flow Centrifugal Pumps: These pumps have an impeller that rotates perpendicular to the pump axis and is used for high-pressure applications.
Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the wide array of centrifugal pumps is immensely valuable when it comes to choosing the ideal pump for specific requirements. To explore the topic further and enhance your knowledge about the different types of centrifugal pumps,
III. Applications of centrifugal pumps
A. Industrial applications
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in industrial applications, such as chemical processing, oil and gas production, and power generation. They are used to transport chemicals, fuels, oils, water, and wastewater. In chemical processing, centrifugal pumps are used to transfer liquids between different process stages, while in oil and gas production, they are used to transport crude oil and natural gas.
B. Domestic applications
Centrifugal pumps are used in domestic applications, such as water supply and HVAC systems. In water supply systems, centrifugal pumps are used to boost water pressure and transport water from a well or a municipal water source to a building’s plumbing system. In HVAC systems, centrifugal pumps are used to circulate water or other fluids through heating and cooling systems, ensuring that the building’s temperature is maintained at a comfortable level.
C. Agricultural applications
Centrifugal pumps are used in agricultural applications, such as irrigation and water management. In irrigation, centrifugal pumps are used to pump water from a well or a water source to a field, providing water for crops. They are also used in livestock farming to pump water to animals in remote locations.
IV. Advantages and disadvantages of centrifugal pumps
A. Advantages
Centrifugal pumps have several advantages, including high efficiency, simple design, low maintenance requirements, and low cost. They can handle a wide range of fluids and can be used in various applications, making them a versatile and essential component in many industries.
B. Disadvantages
Centrifugal pumps also have some disadvantages, such as limited suction lift, low pressure capabilities, and the need for a constant supply of fluid. They can also be prone to clogging and damage from solid particles in the fluid.
V. Maintenance and troubleshooting of centrifugal pumps
A. Maintenance tips
Proper maintenance of centrifugal pumps is essential for ensuring their longevity and efficiency. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the pump for leaks, checking the impeller for wear, cleaning the casing and suction strainer, and lubricating the bearings. It is also essential to check the motor and electrical connections to ensure they are working correctly.
B. Common problems and solutions
Common problems with centrifugal pumps include cavitation, low flow rate, and overheating. Cavitation occurs when the pressure in the pump drops below the vapor pressure of the fluid, causing bubbles to form and collapse, damaging the impeller and casing. Low flow rate can be caused by a clogged suction strainer or a worn impeller. Overheating can be caused by a lack of lubrication or an overloaded motor. Solutions to these problems include increasing the suction head, cleaning the suction strainer, replacing the impeller, and checking the motor and electrical connections.
C. Safety precautions
Safety precautions when working with centrifugal pumps include wearing protective equipment, such as goggles, gloves, and safety shoes, ensuring that the pump is properly grounded, and turning off the power before performing any maintenance or repairs.
VI. Conclusion
Centrifugal pumps are essential components in various industries, and their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility make them a popular choice for pumping liquids. Proper maintenance and safety precautions are critical for ensuring their longevity and safe operation. With continued advancements in technology, centrifugal pumps are likely to remain a vital component in many industries for years to come.
Q1. What are centrifugal pumps, and how do they work?
A1. Centrifugal pumps are mechanical devices that transport fluids by converting mechanical energy into kinetic energy in the fluid being pumped. They work by using a rotating impeller to create a centrifugal force that moves the fluid through the pump and into the discharge pipe.
Q2. What are the basic components of a centrifugal pump?
A2. Centrifugal pumps consist of several basic components, including the impeller, casing, suction and discharge ports, shaft, bearings, and seal. The impeller is a rotating component that transfers energy to the fluid and increases its velocity. The casing is a stationary component that surrounds the impeller and directs the flow of fluid. The suction and discharge ports allow the fluid to enter and exit the pump, respectively. The shaft connects the impeller to the motor and rotates it. The bearings support the shaft and allow it to rotate smoothly, while the seal prevents leaks between the pump and the motor.
Q3. What are the different types of centrifugal pumps?
A3. Centrifugal pumps come in various types, including end suction pumps, inline pumps, multistage pumps, self-priming pumps, and submersible pumps. The choice of pump type depends on the specific application, the desired flow rate, and the head pressure. Single-stage, multi-stage, axial-flow, and radial-flow centrifugal pumps are some of the most commonly used types of centrifugal pumps.
Q4. What are the advantages of using centrifugal pumps?
A4. Centrifugal pumps have several advantages, including high efficiency, simple design, low maintenance requirements, and low cost. They can handle a wide range of fluids and can be used in various applications, making them versatile and essential component in many industries.
Q5. What are the applications of centrifugal pumps?
A5. Centrifugal pumps are widely used in industrial, domestic, and agricultural applications. They are used to transfer fluids such as water, chemicals, fuels, and oils from one place to another. In industrial applications, centrifugal pumps are used in chemical processing, oil and gas production, and power generation. In domestic applications, they are used in water supply and HVAC systems, while in agricultural applications, they are used in irrigation and water management.
Recent Posts

A Comprehensive Guide to Types of Water Pumps and Their Applications
Introduction Water pumps are indispensable

The Complete Guide to Water Pumps: Types, Uses, and Maintenance
Water is life, and the

Comprehensive Guide to Split Case Pumps
Split case pumps are a